Logic and Control Flow
Now that we understand the basics of storing data and interacting with the document and window, we can dive into how to implement logic and decision making in our programs.
The Window Object (Part 2)
Here are two methods associated with the window object that can used to get and display data to the user.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
window.alert(message) | Opens a popup with the message. |
window.prompt(message) | Opens a popup with the message and a input box for the user. |
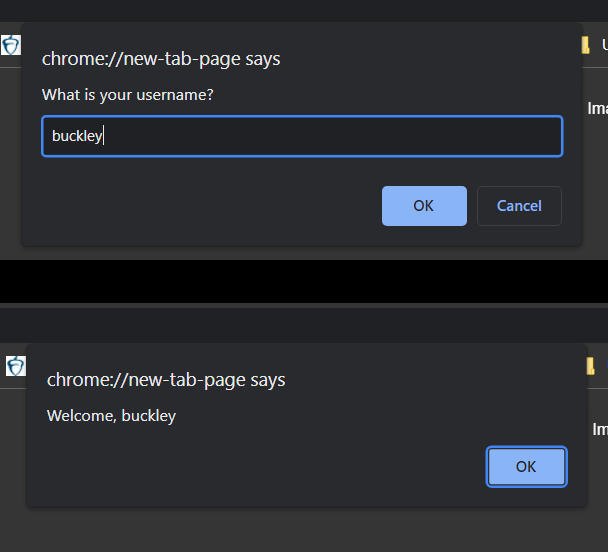
For example, here’s a short program that would allow a user to input their username to a site. The site would then give them a message.
const username = window.prompt("What is your username?")
// You can combine strings and variables with the "+" operator
window.alert("Welcome, " + username)
Result:
Conditionals
A conditional is an if-then statement. In code, they are made up of two main parts: the condition and the body.
if (condition is true) {
// do the body
}
A JavaScript if statement requires the parentheses () around the condition. The curly braces {} for the body are always required for when the body is multiple lines of code and optional if the body is a single line.
If there are two options, you can have an if/else statement:
if (condition) {
// do this if condition is true
} else {
// otherwise, do this
}
Conditions and Boolean Expressions
Here’s an example of how an if/else statement can extend our username getting program to a username validator, giving the user a different message depending on if they type in "steve" or not.
const username = window.prompt("What is your username?")
if (username === "steve") {
window.alert("Welcome, " + username)
} else {
window.alert("Invalid username.")
}
Notice the condition: username === "steve". This is a boolean expression, or a statement that evaluates to true or false. Here are some common boolean operators used in boolean expressions to make comparisons.
| Operator(s) | Description |
|---|---|
! | Not, flips the boolean (i.e. !true equals false). |
>, < | Greater than, Less than. |
>=, <= | Greater than or equal to, Less than or equal to. |
== | Check equivalence without worrying about the type. (2 == '2' is true). |
=== | Check equivalence including type. (2 === '2' is false). |
!= | Not equal (no type checking). |
!== | Not equal (with type checking). |
&& | Logical AND, used to combine multiple boolean expressions. |
|| | Logical OR, used to combine multiple boolean expressions. |
NOTE: For now, just always use
===instead of==. Same goes for using!==instead of!=. It’s safer to always check the type along with the value of the data.
Example with else if and || (OR).
Note that if one condition is satisfied, the rest of the else ifs and elses are skipped.
const direction = window.prompt("Choose N, S, E, or W.")
// If the user typed in "N" or "S", the body of this if will run.
if (direction === "N" || direction === "S") {
window.alert("You can't go that way.")
} else if (direction === "W") {
window.alert("You are in the inner sanctum.")
} else if (direction === "E") {
window.alert("You are in the outer sanctum.")
} else {
// else is usually used as a catch-all
window.alert("Invalid direction")
}
Extra Practice
Practice Task: Quiz Game
Make a Quiz Game where you ask the user questions and they get points for correct answers. Your game must have the following features:
- Have a variable at the top of the program keeping track of score. 2 pts
- Use
window.prompt()for user input, asking the user a multiple-choice question. 2 pts - Have at least 3 conditionals (if/else or if/else if/else statements). Each condition handles user input and adds points to the score if they choose correctly. 6 pts
- Print the score to the player at the end either in the HTML of the document or with an alert. 2 pts
- Provide at least one visual surprise for the player if they win or lose by modifying the DOM. This could be changing the background color, dynamically adding an image, etc. 3 pts
Example
let score = 0
const answer1 = window.prompt(
"What is my favorite color? 'blue', 'red', 'yellow', or 'green'?"
)
if (answer1 === "blue") {
score += 1
window.alert("Correct!")
} else {
window.alert("Incorrect.")
}