NOTE: If you are in the App and Web Development class at Merit, this page is extra.
Next.js Blog Tutorial - Part 5
Learn how to store and retrieve comments using an API and a database.
Starting code: https://replit.com/@buckldav/next-tut-4.
Comments on a Blog
Databases
Most blogs have the ability for visitors to leave comments on posts. These comments are stored in a database on the website’s server. Databases are used in websites whenever there is information that…
- Can be changed.
- Can be accessed by specfic users or the public.
Some popular traditional (SQL) databases include SQLite, MySQL, PostgreSQL, Microsoft SQL Server. Some popular noSQL databases (which are sometimes used by newer technologies) include Google Firebase, Amazon DynamoDB, mongoDB, GraphQL. If you want to learn more about databases, I would suggest trying a SQL database first like SQLite. Learn more at https://www.w3schools.com/sql/.
Repl’s Database
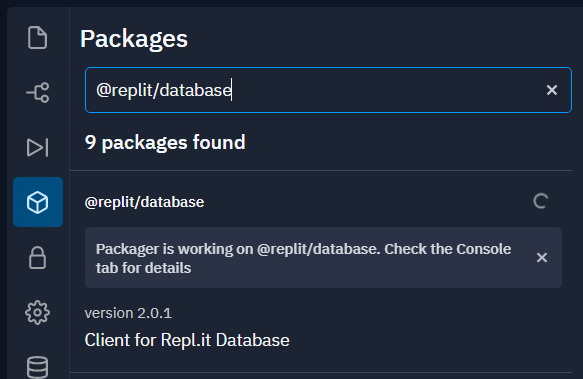
Repl has a built-in database we can use for our blog. We have to first add it to our project by clicking on “Packages” in repl’s left sidebar and searching for @replit/database. Click the + to add the package.
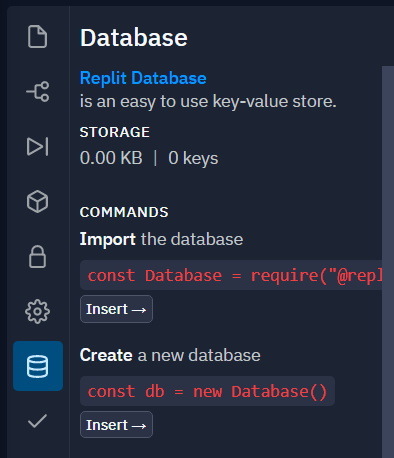
If you click on the database icon in repl’s sidebar, you will see the JavaScript code that can allow you to access the database. We will add some of this code to our project soon.
Accessing Data with an API
An API (Application Programming Interface) is a layer in an application that allows a client to access data and features from a server. In our program, we will create and retrieve comments on the database through an API.
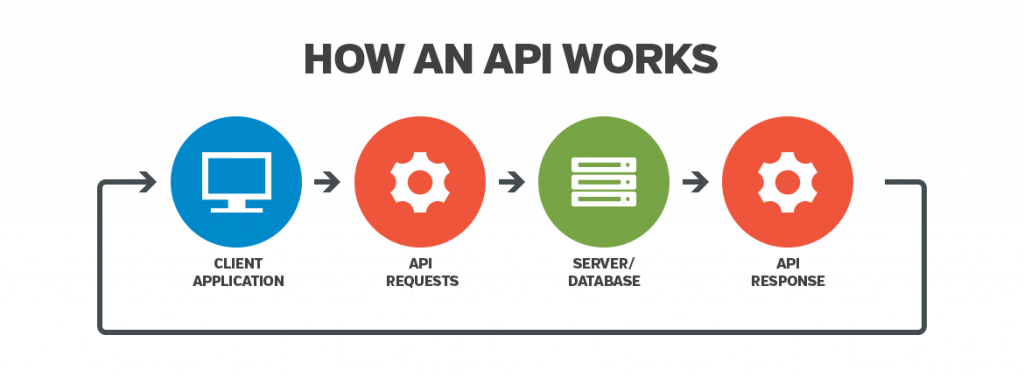
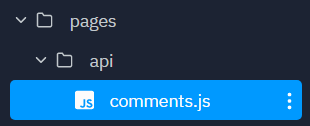
In Next.js, there is an API layer in the pages/ folder. Rename the pages/api/hello.js file to comments.js.
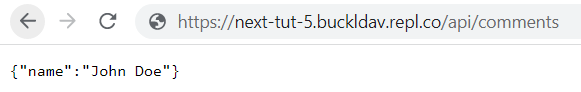
Now, whenever you visit the URL /api/comments, you will see a JSON object like this: {name: "John Doe"}. Recall that file names determine URL paths (api/comments.js becomes /api/comments). We will modify our code so that we can retrieve and add comments instead.
Creating a Comment
In components/Blog.js, add this <form> to the bottom of the <main> component (under the <article>).
<main>
<article>...</article>
<form method="POST" action="/api/comments">
<fieldset>
<legend>Leave a Comment</legend>
<input name="name" placeholder="Anonymous" />
<textarea name="content" rows="3" />
</fieldset>
<input type="submit" value="Submit" />
</form>
</main>
The method="POST" attribute on the form means that the form is for sending data (POSTing data). The action="/api/comments" means that the data will be sent to that URL.
In pages/api/comments.js, we need to add some code so that we can store the data sent from the user interface in our database.
export default async (req, res) => {
if (req.method == "POST") {
// POST request
const res = await fetch(
"https://meritacademy.herokuapp.com/api/comments/",
{
method: "post",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
Authorization: `Api-Key ${process.env.APIKEY}`,
},
body: req.body,
}
)
console.log(await res.json())
}
}
Prevent Redirect to /api/comments on Submit
In components/Blog.js, replace the form’s opening tag with this to prevent the page from redirecting on submit (done with the onSubmit prop).
<form method="POST" action="/api/comments" onSubmit={e => e.preventDefault()}>