Scripting: Finishing our Platformer
Let’s add some code to control our player. Select the Player from the Hierarchy and Add a Script Component called “PlayerController”.
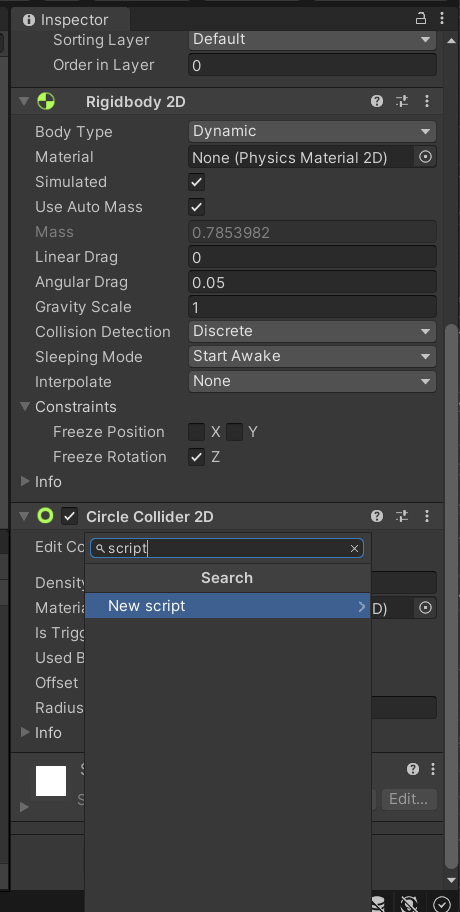
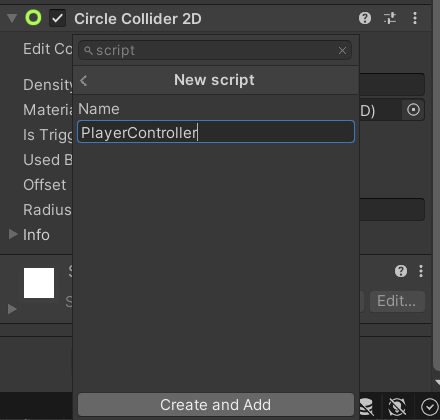
The script will be placed in the Assets folder. Double-click on it to open it in your C# code editor.
Default Script
Start() and Update()
For code that you want to run once, put it in the Start() method. For code that you want to run every frame (like animations), put it in the Update() frame.
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class PlayerController : MonoBehaviour
{
// Start is called before the first frame update
void Start()
{
}
// Update is called once per frame
void Update()
{
}
}
Variables and FixedUpdate
We will need some variables to reference the data that we will be using. For example, the Rigidbody2D rb will be a reference to the Rigidbody2D attached to our Player. Variables should be private unless you want to be able to set them in the Unity Inspector later.
Additionally, we will replace void Update() with void FixedUpdate(), which gets called every frame like Update() but is used for physics.
public class PlayerController : MonoBehaviour
{
private bool isGrounded;
private Rigidbody2D rb;
// Public variables are set in the Unity Inspector
public float xSpeed;
public float jumpStrength;
// Initialize all private variables in Start
void Start()
{
isGrounded = false;
rb = GetComponent<Rigidbody2D>();
}
// FixedUpdate is used for physics (Rigidbody2D)
void FixedUpdate()
{
}
}
Add horizontal movement
Here’s the code for horizontal movement. I’ll walk through it step by step below.
void FixedUpdate()
{
float xHat = new Vector2(Input.GetAxis("Horizontal"), 0).normalized.x;
float vx = xHat * xSpeed;
rb.AddForce(transform.right * vx);
}
float xHat = new Vector2(Input.GetAxis("Horizontal"), 0).normalized.x;
floatis a data type for decimals.Vector2is a object that can store anxandyvalue.newcreates that object.Input.GetAxis("Horizontal")gets the input from the keyboard (Left/Right Arrows, A/D by default)..normalized.xmakes it so that we get1for pushing left (positive x) and-1for pushing right (negative x).
float vx = xHat * xSpeed;
rb.AddForce(transform.right * vx);
Because xHat is just a positive or negative 1, multiplying it by xSpeed will create a value for the velocity vx that sends the player left or right when added as a force to the Rigidbody.
Add vertical movement
void FixedUpdate()
{
float xHat = new Vector2(Input.GetAxis("Horizontal"), 0).normalized.x;
float vx = xHat * xSpeed;
rb.AddForce(transform.right * vx);
float yHat = new Vector2(0, Input.GetAxis("Vertical")).normalized.y;
if (isGrounded && yHat == 1) {
float vy = yHat * jumpStrength;
isGrounded = false;
rb.AddForce(transform.up * vy);
}
}
void OnCollisionEnter2D(Collision2D collision)
{
// You can get rid of the Debug.Log when you want
Debug.Log(collision.gameObject.tag);
isGrounded = collision.gameObject.tag == "Ground";
}
if (isGrounded && yHat == 1) {
float vy = yHat * jumpStrength;
isGrounded = false;
rb.AddForce(transform.up * vy);
}
We only want to move vertical (jump) if we are touching the ground AND the player’s input is up. If both of those conditions are true, we will add a vertical force to the Rigidbody.
void OnCollisionEnter2D(Collision2D collision)
This method executes whenever the player collides with something. We can check to see if the collision object’s tag is “Ground” and enable/disable jumping accordingly.
Final Code
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class PlayerController : MonoBehaviour
{
private bool isGrounded;
private Rigidbody2D rb;
// OPTIONAL: include if you want to limit x velocity
private float maxVelX = 10;
public float xSpeed;
public float jumpStrength;
void Start()
{
isGrounded = false;
rb = GetComponent<Rigidbody2D>();
}
void FixedUpdate()
{
float xHat = new Vector2(Input.GetAxis("Horizontal"), 0).normalized.x;
float vx = xHat * xSpeed;
rb.AddForce(transform.right * vx);
float yHat = new Vector2(0, Input.GetAxis("Vertical")).normalized.y;
if (isGrounded && yHat == 1) {
float vy = yHat * jumpStrength;
isGrounded = false;
rb.AddForce(transform.up * vy);
}
// OPTIONAL: include if you want to limit x velocity
rb.velocity = new Vector2(Vector2.ClampMagnitude(rb.velocity, maxVelX).x, rb.velocity.y);
}
void OnCollisionEnter2D(Collision2D collision)
{
isGrounded = collision.gameObject.tag == "Ground";
}
}
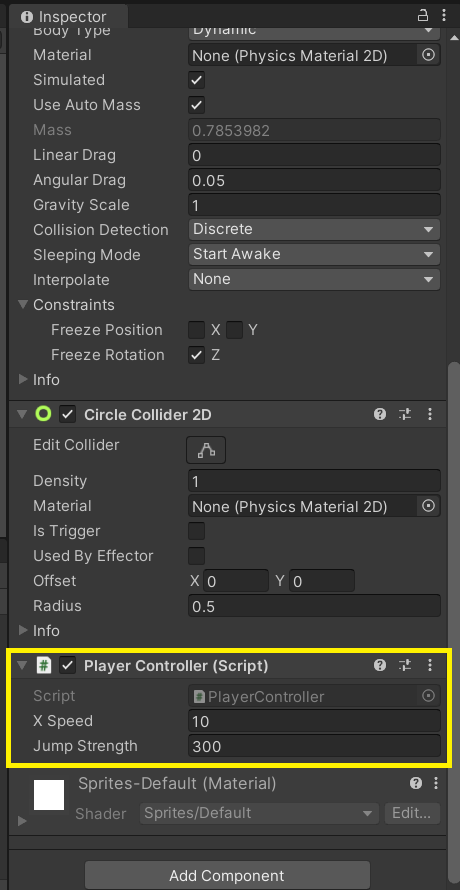
Setting Your Public Variables in the Inspector
In the Unity Inspector, you’ll see X Speed and Jump Strength from your public variables in your script. Test out different values unitl you like them. You might also consider adjusting drag and gravity in the Rigidbody.
Final Game
Here’s an example of the final game.